 deploy software via GPO " width="" />
deploy software via GPO " width="" />In this article, we will show how to install software on user computers in an Active Directory domain using GPO.
The built-in Windows GPO features allow you to deploy programs that are only distributed as MSI or ZAP packages. Other types of apps you will have to install in alternative ways: using SCCM, via GPO logon scripts, copying program files to computers using GPO, running one-time scripts, etc.
Let’s see how to install the MSI software package on users’ computers via Windows Group Policies on the example of the Microsoft Teams client.
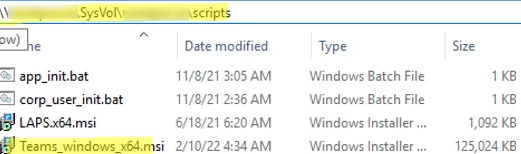
Download the MSI package with the Teams client (http://aka.ms/teams64bitmsi) and copy Teams_windows_x64.msi to the SYSVOL folder on the domain controller ( \\woshub.com\SysVol\woshub.com\scripts ).
 deploy software via GPO " width="" />
deploy software via GPO " width="" />
Please note that there are x86 and x64 MS Teams versions. If you still have computers running x86 versions of Windows, you will need to create a separate GPO for x86 and x64 computers. You can use GPO WMI filters to filter Windows versions in Group Policies.
Many apps are not provided in a form of MSI packages. Most often, developers distribute them as EXE files that are not suitable for deployment through GPO. However, in some cases, you can extract the MSI package from the EXE installation file:
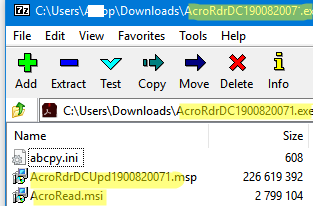 Extracting MSI from EXE installation" width="" />
Extracting MSI from EXE installation" width="" />
Then create a new domain Group Policy Object to install your software.
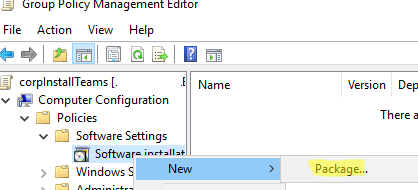
The Assigned option allows installing apps at the user logon. The Published option publishes apps to computers and users can install them in Add/Remove Programs.
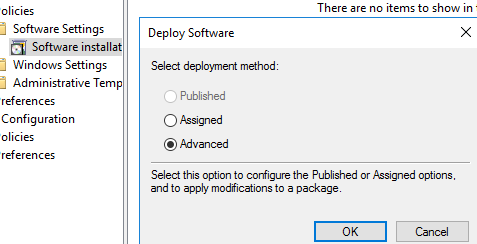

If the software deployment GPO doesn’t apply to target computers, use the troubleshooting tools described in the article Why a Group Policy Is not Applied to a Computer and the gpresult command.
You cannot specify installation keys or parameters for MSI installation packages in the standard GPO interface. For example, when installing an anti-virus agent on a user’s computer, you must specify the IP address/FQDN of the management server. Or, when you install Teams from the command prompt using msiexec, you can disable the MS Teams client automatic startup and hide it from the list of installed apps (a local administrator won’t be able to remove the Teams client). To do it, the following command is used:
msiexec /i Teams_windows_x64.msi OPTIONS="noAutoStart=true" ALLUSERS=0
How to add setup options to an MSI package? To do it, MST transformation files are used. This file type allows you to change the default MSI package settings and use your installation scenario.
To create an MST file for an MSI package, you can use the ORCA tool (it is a part of Windows Installer SDK ).
Open your MSI package using Orca.
Create a New Transformation and set your custom MSI package options in the Property section. I will change the following options for my Teams client:
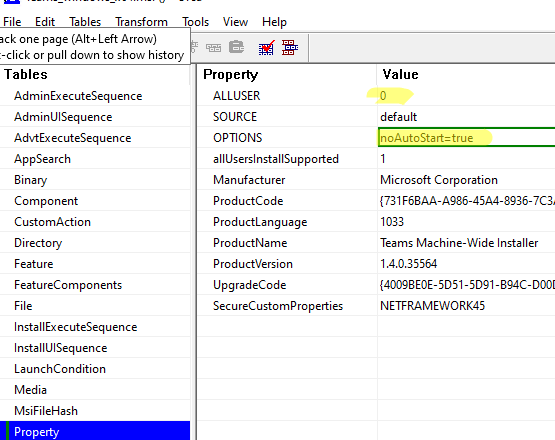 the Orca MSI editor " width="" />
the Orca MSI editor " width="" />
Select Transform -> GenerateTransform and save the changes as MST file ( teams_mod.mst ). Copy the file to the SYSVOL directory.
Then remove the previous rule to install the MSI package in the GPO (because you can add an MST file with package modifications only when creating an app installation rule).
Select All –> Task -> Remove.
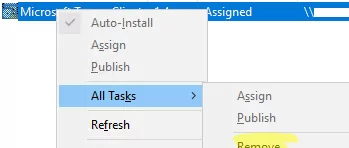
Create a new software deployment rule, select the MSI file from SYSVOL, and go to the Modification tab. Click Add. Select the MST file you created earlier.
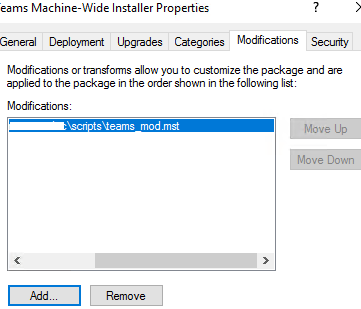
The MST file will now be automatically applied during the MSI installation using the GPO and the application will be installed with the settings you need.
The main disadvantages of MSI installation through GPO: